The world is more connected and digital than ever. While this brings countless benefits, it also creates a significant problem—e-waste. This issue is especially relevant in Bangladesh, where e-waste is growing at an alarming rate.
Bangladesh is rapidly urbanizing, with the demand for electronics surging in both households and industries. As a result, e-waste in Bangladesh has become an urgent environmental and health issue. But how do we manage this growing challenge? Let’s take a deep dive into the e-waste problem in Bangladesh, why it’s so dangerous, and how we can move toward a more sustainable solution.
What Is E-Waste?
E-waste refers to discarded electronic devices that are no longer usable. This includes everything from mobile phones and laptops to large appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners. These devices often contain harmful substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into the environment if not disposed of properly.
The most common sources of e-waste include:
- Computers and mobile phones
- Televisions
- Refrigerators and air conditioners
- Printed circuit boards
Bangladesh, like many developing countries, is experiencing rapid growth in electronic waste due to the widespread use of digital technologies and rising incomes. The challenge is how to manage this growing pile of discarded electronics safely and efficiently.
The Scale of the E-Waste Problem in Bangladesh
How Much E-Waste Is Produced in Bangladesh?
Bangladesh is currently generating thousands of tons of e-waste each year. According to a report by the Department of Environment, around 400,000 tons of e-waste were produced in 2020, and this number is expected to grow as more people have access to electronic devices.
This e-waste includes discarded mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and large appliances. The demand for these items is increasing, which means the amount of e-waste generated will continue to rise in the coming years.
Why Is E-Waste Dangerous?
E-waste is more than just an inconvenience. It poses serious risks to both the environment and human health. Here’s why:
1. Toxic Chemicals
E-waste contains hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium. When disposed of improperly, these toxic materials can contaminate soil and water. They can harm the ecosystem and enter the food chain, affecting not only wildlife but humans as well.
2. Air Pollution
Improper disposal of e-waste, such as burning it in open air, releases toxic fumes into the atmosphere. These fumes contain dioxins and furans, both of which are harmful to human health and contribute to air pollution.
3. Impact on Workers’ Health
In Bangladesh, a significant portion of e-waste recycling is done in the informal sector, where workers handle toxic substances without any protective gear. This leads to severe health problems, including respiratory issues, skin diseases, and in extreme cases, cancer. The risks to e-waste workers are enormous.
Current E-Waste Management in Bangladesh
How Is E-Waste Currently Handled?
In Bangladesh, most e-waste is either sent to landfills or recycled through the informal sector. Informal recyclers dismantle electronic devices by hand, often without proper tools or protective equipment. This practice exposes workers to harmful chemicals and releases toxins into the environment.
The informal recycling sector is a significant player in the e-waste economy, but it comes with numerous downsides. Without proper safety measures, informal recycling is dangerous both for workers and the environment.
The government of Bangladesh has recognized this problem and has introduced the E-Waste Management Rules 2021. These rules aim to regulate e-waste collection and recycling, encouraging formal, environmentally friendly methods of disposal. However, implementation remains a challenge.
Government Regulations: E-Waste Management Rules 2021
The E-Waste Management Rules 2021 are a step in the right direction. This legislation introduces guidelines for the safe disposal, collection, and recycling of e-waste. It also requires manufacturers to take responsibility for the disposal of their products after they are no longer usable.
The law is aimed at reducing the environmental impact of e-waste and ensuring that recyclers follow proper safety measures. The hope is that these rules will help move the country away from informal recycling practices and toward a more sustainable e-waste management system.
The Role of the Informal Sector in E-Waste Recycling
How the Informal Sector Operates
The informal recycling sector is a crucial part of Bangladesh’s economy. Workers in this sector collect discarded electronics from households and industries, often breaking them apart manually to extract valuable materials like copper, aluminum, and gold. These materials are then sold to scrap dealers for a profit.
While this practice helps recover valuable resources, it is highly inefficient and dangerous. Workers are exposed to toxic chemicals without any protective gear, leading to severe health risks. Moreover, the process often releases harmful substances into the environment, contributing to air and soil pollution.
How Can We Transition to Formal Recycling?
A shift from the informal to the formal recycling sector is essential for the safe management of e-waste in Bangladesh. Formal recycling facilities use advanced technologies to dismantle and recycle electronic devices. These facilities are safer for workers and more efficient at recovering valuable materials.
Steps Toward Formal Recycling
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: The government needs to launch awareness campaigns to educate people about the dangers of improper e-waste disposal. This will encourage individuals and companies to use formal recycling services.
- Incentives for Recycling: The government can offer tax breaks or other incentives to businesses that set up formal e-waste recycling facilities.
- Enforcement of Laws: Strict enforcement of the E-Waste Management Rules 2021 is necessary to ensure that informal recycling practices are phased out.
- Public-Private Partnerships: By partnering with private companies, the government can set up a network of e-waste collection centers across the country, making it easier for people to dispose of their electronic waste responsibly.
E-Waste and the Circular Economy
One promising solution to the e-waste problem is adopting a circular economy model. In a circular economy, products are designed to last longer, be reused, and eventually recycled at the end of their life cycle. This reduces the need for new raw materials and minimizes waste.
How the Circular Economy Can Help
By transitioning to a circular economy, Bangladesh can reduce the amount of e-waste generated while also recovering valuable materials. Electronics manufacturers can design products that are easier to repair and recycle, ensuring that fewer devices end up in landfills.
Global Best Practices for E-Waste Management
Several countries have successfully implemented e-waste management policies that Bangladesh can learn from.
1. Japan
Japan has one of the most advanced e-waste recycling systems in the world. The country requires manufacturers to take back their products once they are no longer useful, encouraging the reuse and recycling of valuable materials.
2. The European Union
The European Union’s WEEE Directive (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) sets strict guidelines for the collection, recycling, and disposal of e-waste. Under this directive, manufacturers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, from production to disposal.
3. China
China has introduced a nationwide e-waste collection system, providing designated drop-off points where individuals can safely dispose of their electronic waste.
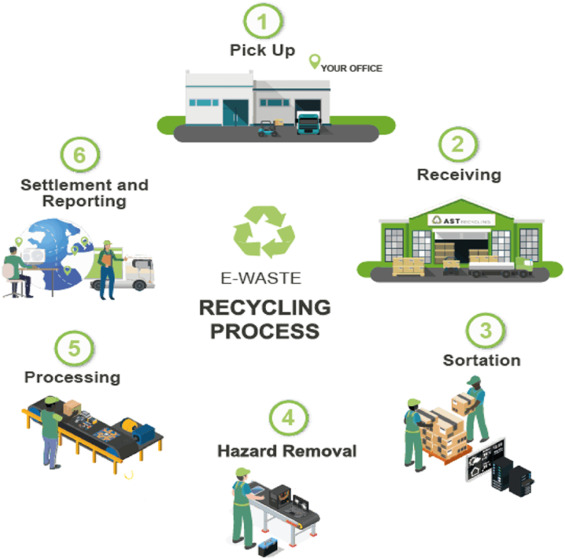
How to Recycle E-Waste in Bangladesh: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you’re wondering how to properly dispose of your electronic waste in Bangladesh, here’s a simple guide:
Step 1: Find an Authorized Recycler
Search for a formal recycling facility or a collection point authorized by the Department of Environment. These centers ensure safe handling and recycling of e-waste.
Step 2: Separate Your Electronics
Before recycling, separate your electronics by type (e.g., mobile phones, laptops, large appliances). This will help recyclers process your e-waste more efficiently.
Step 3: Wipe Personal Data
Before discarding any electronic device, make sure to delete all personal data. You can do this by performing a factory reset or using data-erasing software.
Step 4: Drop Off at the Collection Center
Take your separated e-waste to the designated e-waste collection point. Ensure that the recycler follows proper disposal practices in compliance with the E-Waste Management Rules 2021.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the efforts to manage e-waste in Bangladesh, several challenges remain:
- Lack of infrastructure: There are not enough formal recycling centers to handle the growing volume of e-waste.
- Public awareness: Many people are unaware of the dangers posed by e-waste or the proper disposal methods.
- Enforcement of laws: While the E-Waste Management Rules 2021 are a step in the right direction, enforcement remains weak.
However, by investing in infrastructure, raising public awareness, and enforcing existing regulations, Bangladesh can make significant progress toward sustainable e-waste management.
Conclusion: The Future of E-Waste in Bangladesh
E-waste in Bangladesh is a pressing issue, but it’s not an unsolvable one. With the right mix of government regulation, private sector investment, and public awareness, we can move towards a more sustainable future.
The transition to a circular economy, combined with stricter enforcement of the E-Waste Management Rules 2021, will go a long way toward reducing the environmental and health risks associated with electronic waste.
By recycling and properly disposing of our electronics, we can help create a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable Bangladesh.
FAQs: Common Questions About E-Waste in Bangladesh
1. What is the biggest source of e-waste in Bangladesh?
The biggest sources are mobile phones, computers, and large appliances like refrigerators.
2. Why is e-waste dangerous?
E-waste contains hazardous materials like lead and mercury, which can harm human health and the environment.
3. How can I safely dispose of e-waste?
Take your e-waste to an authorized recycling facility or drop-off point in compliance with the E-Waste Management Rules 2021.
4. What are the government’s efforts to tackle e-waste?
The E-Waste Management Rules 2021 provide guidelines for the safe disposal, collection, and recycling of e-waste.
Leave a Reply